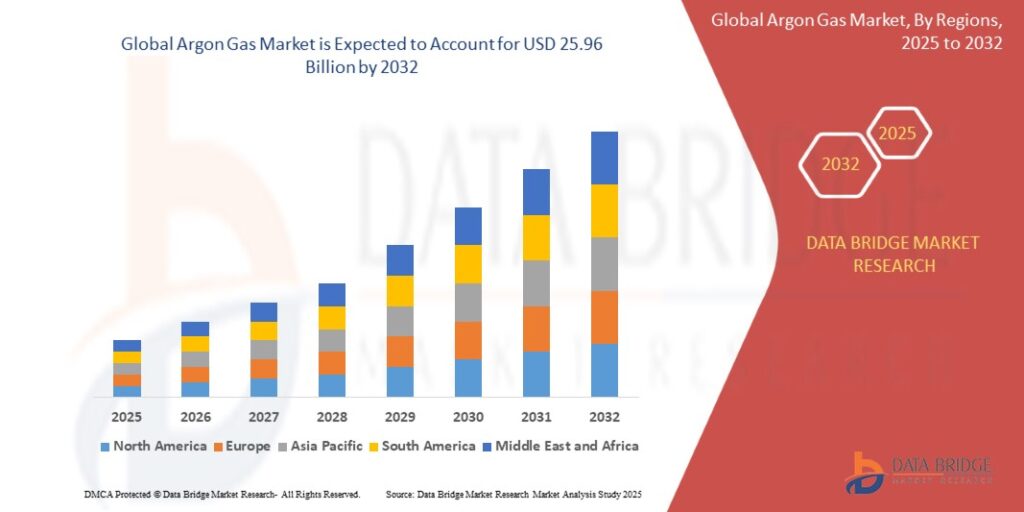
Introduction
Argon gas, a noble gas found in Earth’s atmosphere, plays a crucial role in various industries, from welding and electronics to healthcare and lighting. As an inert gas, it is widely used for shielding and protective applications, ensuring stability in processes where other gases might react undesirably.
This blog explores the properties, uses, market trends, and future outlook of argon gas, shedding light on its growing significance in industrial and scientific applications.
What Is Argon Gas?
Argon (symbol: Ar, atomic number: 18) is a colorless, odorless, and non-toxic noble gas that makes up approximately 0.93% of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is produced commercially by fractional distillation of liquid air in cryogenic air separation plants.
Key Properties of Argon Gas
- Inert and Non-Reactive – Does not readily react with other elements or compounds.
- Colorless and Odorless – Invisible and undetectable without specialized equipment.
- Heavier than Air – Settles in low-lying areas in confined spaces.
- Non-Toxic and Non-Flammable – Safe for use in various industries with proper handling.
- Low Thermal Conductivity – Provides excellent insulation in windows and industrial applications.
Applications of Argon Gas
1. Welding and Metal Fabrication
Argon is widely used in welding processes, such as:
- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding – Ensures clean, high-quality welds on stainless steel, aluminum, and magnesium.
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding – Mixed with other gases (CO₂, oxygen) to optimize arc stability and penetration.
- Plasma Cutting and Laser Welding – Used as a shielding gas to prevent oxidation and contamination.
2. Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
- Used in the manufacturing of semiconductors, microchips, and flat-panel displays.
- Provides an oxygen-free environment for producing high-purity silicon and other materials.
3. Healthcare and Medical Applications
- Used in cryosurgery to remove tumors and abnormal tissues.
- Acts as a carrier gas in medical imaging and MRI spectroscopy.
- Inert atmosphere for preserving biological samples and drugs.
4. Lighting and Lasers
- Used in incandescent and fluorescent light bulbs to prevent filament degradation.
- Employed in argon-ion lasers, widely used in medical, scientific, and industrial applications.
5. Food and Beverage Industry
- Extends the shelf life of packaged foods by displacing oxygen and preventing oxidation.
- Used in wine bottling to preserve freshness and flavor.
6. Aerospace and Automotive Industry
- Creates an inert atmosphere for titanium and aluminum production.
- Used in 3D printing of metal components, ensuring high-quality results.
7. Insulation and Windows
- Fills double-glazed windows to enhance thermal insulation and reduce energy loss.
- Reduces condensation and prevents frost formation on windows.
Argon Gas Market Trends and Growth Factors
1. Increasing Demand in Metal Fabrication
- Growth in construction, automotive, and aerospace sectors drives the need for argon in welding and metalworking.
2. Expanding Semiconductor and Electronics Industry
- The rise of consumer electronics, AI, and IoT devices is fueling demand for high-purity argon in semiconductor production.
3. Advancements in Healthcare and Cryogenic Applications
- Growth in medical technologies, cryosurgery, and imaging techniques is expanding the role of argon in healthcare.
4. Energy-Efficient Building Materials
- Increasing focus on energy conservation is boosting the use of argon in insulated windows.
5. Rising Demand for Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
- The use of argon in metal 3D printing ensures superior material quality, driving its adoption in advanced manufacturing.
Challenges in the Argon Gas Market
1. High Production and Storage Costs
- The cryogenic separation process requires significant energy and infrastructure investment.
2. Supply Chain Limitations
- Argon gas production is dependent on oxygen and nitrogen production, creating supply fluctuations.
3. Safety and Handling Concerns
- Although non-toxic, argon can displace oxygen in confined spaces, posing asphyxiation risks.
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-argon-gas-market
Future Outlook of Argon Gas
With advancements in manufacturing, healthcare, and energy-efficient technologies, the demand for argon gas is expected to grow steadily. Innovations in air separation techniques, recycling processes, and improved storage solutions will further enhance its accessibility and affordability.
Conclusion
Argon gas is an indispensable resource across numerous industries, from welding and semiconductors to healthcare and insulation. Its inert properties make it a valuable tool for ensuring stability, longevity, and efficiency in various applications. As industries continue to evolve, argon will remain a key component in technological advancements and sustainable innovations.